Key takeaways
-
Since the Fibonacci scale is an exponential sequence of numbers, it is often used in Agile planning to estimate work that needs to be done.
-
Fibonacci numbers give more realistic estimates for highly complex tasks.
-
Use the Fibonacci scale in Agile estimation to assign story points to work items.
Chances are that you’ve had the experience of being given an estimate that turned out to be completely wrong. For example, your car wasn’t repaired in two days, or the table at the restaurant wasn’t ready in 15 minutes.
If estimates can be inaccurate, why are they important to project planning?
It’s a matter of setting the right expectations and determining how much work is realistic to complete in a given timeframe. Teams need to account for a project’s complexity in order to decide the amount of effort required, the number of resources needed, and ultimately, how much time it will take to complete the project.
Many Agile teams have successfully improved their estimation process by using the Fibonacci scale or a modified Fibonacci sequence to estimate the work that needs to be completed in an iteration.
Learn what the Fibonacci sequence is and how you can apply it to your team’s Agile estimation techniques.
What is the Fibonacci sequence?
Fibonacci was an Italian mathematician during the Middle Ages who wrote a book called “Liber Abaci (Book of Calculation).” In “Liber Abaci,” Fibonacci presented the following problem:
A certain man put a pair of rabbits in a place surrounded on all sides by a wall. How many pairs of rabbits can be produced from that pair in a year if it is supposed that every month, each pair begets a new pair, which from the second month on becomes productive?
To estimate the answer, Fibonacci introduced an exponential sequence of numbers, now known as the Fibonacci number or the Fibonacci sequence. In the sequence, each number is the sum of the preceding two numbers:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, etc.
The Fibonacci sequence is found in many different disciplines and in nature. For example, it has been used to describe plant growth, estimate population increases over a specified time frame, and model virus breakouts.
Why is the Fibonacci sequence used in Agile?
The Fibonacci scale gives Agile teams a more realistic way to approach estimates as they plan work to be done during a certain period of time (such as a sprint). Teams often use story points to represent the size, complexity, and effort needed to complete a user story. They assign each story point a number from the Fibonacci scale. The higher the number, the more complex, and presumably, the more amount of effort it will take to complete.
For example, if you need to change the color of a CTA button on a page of your website, that task may rank lower in effort and be assigned one story point. Another task, such as introducing a social login feature (logging in with an Apple or Google account) to an existing application, may rank higher and be assigned eight story points. Larger tasks are typically broken down into smaller tasks or distributed among several team members to work on.
As discussed previously, estimates can often be inaccurate, which often occurs because people tend to be overly optimistic. People often believe they can complete a task faster if they’ve done it before or believe there won’t be any delays. Because the Fibonacci scale is exponential rather than linear, it helps teams to be more realistic when looking at larger, more complex tasks. By using the Fibonacci scale for Agile estimation, teams can more easily recognize the differences between tasks and define complexity with exponentially larger story points.
How to use the Fibonacci sequence in Agile estimation
Many teams use numbers from the Fibonacci scale during planning poker or other team estimation activities as they assign story points and other units of estimation to work items. If you don’t have physical cards to show numbers (or you have a distributed team), you can host an estimation activity virtually using a Fibonacci scale template. An online Fibonacci scale is a great solution for distributed teams who can’t physically meet in the same location.
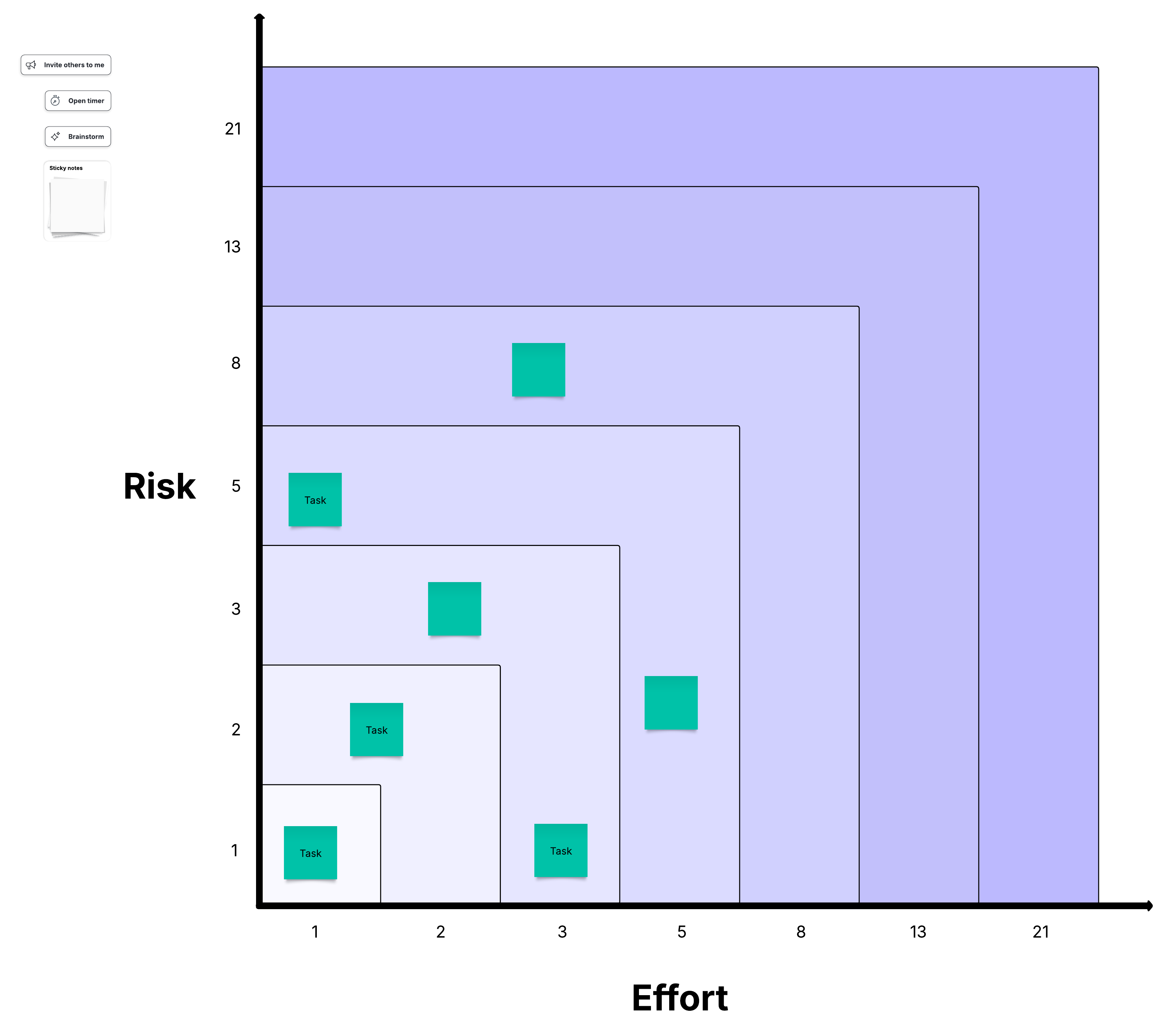
You can also try a task estimation template to guide your discussion as you refine and estimate tasks from your backlog. In the template below, you can use story points with Fibonacci numbers to discuss several tasks with your team. Remember, Agile estimation is a group effort. Your whole team should be involved, and everyone should understand what numbers from the Fibonacci scale mean.

Benefits of using Fibonacci Agile estimation
As you use the Fibonacci sequence in Agile estimation, your team can experience the following benefits:
-
Ensure that everyone has a voice. The whole team should be involved in the Agile estimation process, which invites everyone to provide input. Each team member gives a different perspective that helps to hone in on a more accurate and realistic estimation of the work required to complete a user story.
-
Establish a scale for comparing story point complexity. Assigning story points with linear numbers makes it difficult to determine the weight each story point should carry, but the exponential nature of the Fibonacci scale makes it easy for the entire team to understand what the assigned numbers mean. For example, a story point assigned the number one could mean that complexity is minimal and that several of these tasks could be completed in a day. A 13, however, means the story point is very complex, and everyone should understand that the task could take weeks to complete.
-
Improve the accuracy of estimates. By using the Fibonacci scale, the team can more realistically look at the complexity and effort required to complete a task, and over time, this can lead to more accurate estimates. When teams improve their accuracy, they can more realistically commit to deadlines and deliver projects on time.
Ready to start using the Fibonacci scale and improve your estimation technique? Incorporate Fibonacci numbers into your Agile planning processes to boost understanding, team cohesion, and ultimately, agility as you commit to projects.

Learn more about Agile estimation techniques
Learn more about story points and other units of Agile estimation in our in-depth guide.
Read moreAbout Lucid
Lucid Software is the leader in visual collaboration and work acceleration, helping teams see and build the future by turning ideas into reality. Its products include the Lucid Visual Collaboration Suite (Lucidchart and Lucidspark) and airfocus. The Lucid Visual Collaboration Suite, combined with powerful accelerators for business agility, cloud, and process transformation, empowers organizations to streamline work, foster alignment, and drive business transformation at scale. airfocus, an AI-powered product management and roadmapping platform, extends these capabilities by helping teams prioritize work, define product strategy, and align execution with business goals. The most used work acceleration platform by the Fortune 500, Lucid's solutions are trusted by more than 100 million users across enterprises worldwide, including Google, GE, and NBC Universal. Lucid partners with leaders such as Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft, and has received numerous awards for its products, growth, and workplace culture.
Related articles
How to calculate story points in Agile for improved project planning
Learn how to calculate story points in Agile to improve sprint planning.
Guide: The top Agile estimation techniques to enhance alignment and efficiency
Read about the top Agile estimation techniques and how to choose the one that’s right for your team.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy.
